
22 Jan The Effect of Exercise Training on OSA and Sleep Quality
Exercise and sleep are two aspects of a person’s life can often, especially when poor can be directly linked to many individuals lowered health.
So how well do they interact with each other?
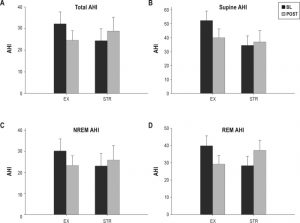
In 2011, (Kline, C & et al) conducted a randomized controlled trial which saw 43 sedentary and overweight/obese participants, aged 18-55 years with at least moderate obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) ≥ 15, completing a 12 week exercise program. Of the 43 – 27 met 4 times a week performing 150 minutes a week of moderate intensity aerobic activity, followed by resistance training twice a week. Whilst the other 16 met twice a week to perform low-intensity exercises designed to increase whole body flexibility.
To confirm the OSA severity requirement as well as monitor the change post interventions, laboratory polysomnography (PSG) was completed.
The results discovered within this study were that compared to base level stretching, exercise resulted in a significant AHI reduction for those in the exercise group. Interestingly, this improvement was captured with a lack of change within the body weight of the participants, with obesity being a massive indicator for OSA development and severity, this shows the strength of exercise is improving OSA severity.
Sleep quality was also measured via a subjective quiz in which a greater proportion of the exercise group reported to have good quality sleep after the intervention compared to the control group.
To the effectiveness of this study, the impact that exercise alone, negating that of weight loss, is already apparent. However, conjoining with long term exercise and steady weight loss indicative diet would likely see even further improvement to this participant groups for improving their OSA severity and overall sleep.
Kline, C. E., Crowley, E. P., Ewing, G. B., Burch, J. B., Blair, S. N., Durstine, J. L., Davis, J. M., & Youngstedt, S. D. (2011). The effect of exercise training on obstructive sleep apnea and sleep quality: a randomized controlled trial. Sleep, 34(12), 1631–1640. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1422

