
25 Oct Choosing an Oronasal Mask with CPAP May Cause Unintended Consequences in Some Patients
Posted at 06:00h
in Blog
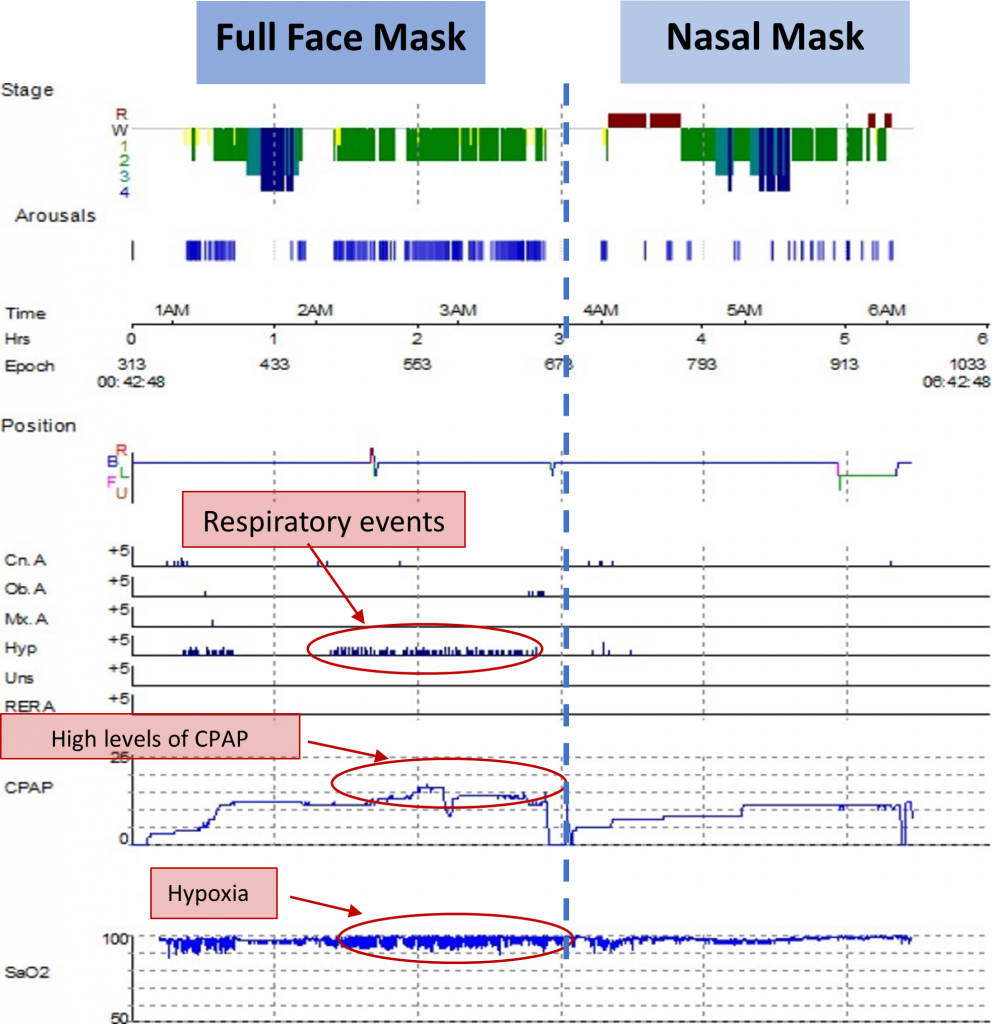
- A 37-y-old man (body mass index [BMI] 28.5 kg/m2) underwent an in-laboratory DSS in which his AHI was recorded at 50 events/h.
- The titration was initially commenced with an oronasal interface. CPAP pressures between 4 and 17.5 cmH2O were trialled for 170 min. There was persistent snoring, obstructive apnoeas and hypopneas at a CPAP pressure of 17.5 cmH2O with an AHI of 55.8 events/h. Maximum mask leak at this CPAP pressure was 78 L/min.
- With the nasal mask, CPAP pressures between 4 and 12 cmH2O were trialled for 130 min. A CPAP pressure of 12 cmH2O with the nasal mask successfully treated UAO, reducing AHI to 3.8 events/h, and stopped all snoring episodes.
- The patient tolerated CPAP well and perceived a better-quality sleep with the nasal mask compared to the oronasal mask. He continued with CPAP treatment at home using a nasal mask.
Author: Luca Maioli (BBioMed, BBus), CPAP Educator

