30 Aug Melatonin receptor type 1A gene linked to Alzheimer’s disease in old age
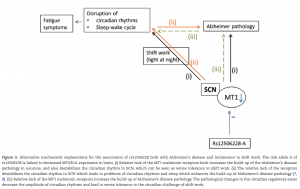
Variant rs12506228A is a genetic variant found close to the code for melatonin receptor 1a (MTNR1A). Sulkava et al. recently published an article in the Journal of Sleep that studies this genetic variant’s association with clinical and neuropathological Alzheimer’s disease. They found that there is an association. This variant was previously shown to be a risk factor for shift work intolerance. However further study is needed to clarify whether poor tolerance to shift work pe se indicates increased risk of Alzheimers disease. The researchers propose that circadian regulation may contribute to pathological cascade of Alzheimers disease.
Statement of Significance
The previous systematic search for molecular genetic risk factors for intolerance to shift work identified a risk variant close to melatonin receptor 1a (MTNR1A). Here, we showed association of the same risk variant with clinical and pathological Alzheimer’s disease in the very elderly. In line, modulation of the MTNR1A expression level in cell culture regulated amyloid beta production. Thus, we revealed a novel molecular genetic connection between circadian phenotype in the working age and neurodegeneration in old age, which supports the view that circadian regulation, possibly through weaker physiological melatonin signalling, contributes to the pathological cascade of Alzheimer’s disease. Future studies are needed to clarify whether the poor tolerance to shift work per se indicates increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Citation:
Sonja Sulkava, Pranuthi Muggalla, Raimo Sulkava, Hanna M Ollila, Terhi Peuralinna, Liisa Myllykangas, Karri Kaivola, David J Stone, Bryan J Traynor, Alan E Renton, Alberto M Rivera, Seppo Helisalmi, Hilkka Soininen, Tuomo Polvikoski, Mikko Hiltunen, Pentti J Tienari, Henri J Huttunen, Tiina Paunio; Melatonin receptor type 1A gene linked to Alzheimer’s disease in old age, Sleep, , zsy103, https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsy103